Prompting
The behaviour of Copilot depends a lot on the mode and LLM (Large Language Model) that you select.
What Are The Default Modes?
Modes restrict or enhance the kinds of work that Copilot can do for you. The four default modes are:
| Mode | Can Change Files | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Agent | Yes | The most powerful mode. In Agent mode, Copilot can analyze any files in your repo, edit and create files, and use MCP servers (if available). |
| Plan | No | This mode is for getting a step-by-step plan to accomplish a task. Copilot will not execute the plan, but it will show you the steps it would take. |
| Ask | No | It will use any open files in VSCode for reference, but it never edits or creates files. All answers go in the chat window. |
| Edit | Yes | In this mode, Copilot can edit any files that are open in VSCode, but it will not try to edit other files in VSCode that are not open. |
Select the mode from the lower left-hand corner of your Copilot chat window in the agent picker menu.
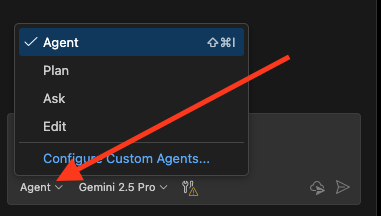
Figure 2: Selecting Copilot Mode
The Ask and Plan modes are good when you're not sure exactly what you need done and you want to get details from Copilot without having it spend time changing your code.
Agent mode is the workhorse mode where the default action is for Copilot to make changes to your files.
The Configure Custom Agents selection in the above screen capture is discussed in the custom agents page
Choosing An LLM To Use
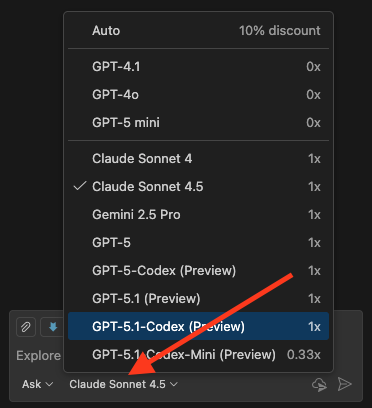
LLMs are the "brain" of your session. You can trivially switch LLMs during any session, and sometimes it's a good idea to have one LLM check another LLM's work. However, for consistency, it's often a good idea to stick with one LLM for an entire session.
There is no one best LLM. However, anecdotal evidence shows that the following has been true:
- Claude - Best for coding and software development tasks like documentation
- ChatGPT - Best for creative writing and business communications (MS365 documents, for example)
- Gemini - Best at data analysis and visualization
The Github docs here have their own opinion about which LLM is best for specific tasks.
Best Practices For Prompting
Use absolute pathnames for files and directories when possible
Copilot will try to search your code base for specific files and directories that it needs (or that you mentioned) in order to complete tasks. This can use up a significant amount of time. By using absolute pathnames for files and directories, it immediately knows where to find them.
Example prompt
Change the filenames in the directory /home/nextjs-web/apps/docs/docs/copilot/images to camel case
You can also use @filename to reference a specific file. For example:
In @UserProfile.tsx add error handling for the API call
Being specific tends to yield better results
The more specific you can be about the versions of apps you want used, your requirements, and even providing examples, the better your results will be. Imagine that you're giving instructions like GPS does (Google Maps, for example).
Example prompt
Create a utility function to format US phone numbers in /home/nextjs-web/packages/utilities/src/formatters/phoneFormatter.ts
Requirements:
- Use TypeScript 5.8 with strict mode enabled
- Create a function named formatPhoneNumber that accepts a string parameter
- Use Zod 3.24 to validate the input is a 10-digit string
- Return formatted string in format: (XXX) XXX-XXXX
- If input is invalid, return the original input unchanged
- Include JSDoc 4.1 comments with @description, @param, and @returns
- Use const for all variables
- Export as named export
- Follow our naming convention: camelCase for function name
- Handle edge cases: null, undefined, empty string, non-numeric characters
- Use optional chaining (?.) for null checks
- Keep the function pure (no side effects)
Example:
Input: "1234567890"
Output: "(123) 456-7890"
Use Plan mode to find out how copilot will proceed
It's not always clear that Copilot will understand what you want done. To make sure that Copilot doesn't spend a lot of time making errors on your behalf, use Plan mode to find out if it understands your request. Then, switch to Agent mode to have it do the work.
Ask Copilot how/why it got a specific result
Any time you get a result from Copilot and you don't understand why, just ask it.
Example Prompt
Why did you add a parameter named findVar when I asked you to refactor this function?
Break complex tasks into smaller steps
Prompting for complicated tasks may lead to suboptimal results as the LLM may not always understand a problem the way that you do. Break the problem into smaller tasks and prompt them one at a time for better results.
Example prompt sequence
1. `Create the interface for UserSettings in /home/nextjs-web/packages/ui/src/types/user.ts`
2. `Now create a validation schema using Zod for that interface`
3. `Create a React component that uses this schema to validate form input`
Provide examples of existing patterns to follow
Reference similar code already in your codebase so Copilot matches your team's style and architecture.
Example prompt
Create a new data transformer for orders following the same pattern as @productTransformer.ts in /home/nextjs-web/packages/transformer/src/
Use iteration to refine unsatisfactory results
If the first result isn't quite right, provide specific feedback about what to change rather than starting over.
Example prompt
The error handling you added is too verbose. Simplify it to just log the error and return null